23-11-2024 - Education - Linear Algebra - Angles and distances in the affine case [EN]-[IT]
2 comments
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
23-11-2024 - Education - Linear Algebra - Angles and distances in the affine case [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to provide some brief notions regarding the technical topic mentioned in the subject.
The context in which we operate is that of analytical geometry or linear algebra
(code notes: MOD-65)
Angles and distances in the affine case
In the affine context, to define a distance between two points, we consider the difference between the position vectors of the points and we measure the norm of the resulting vector.
Distances in the affine case
When we talk about analytical geometry and we are in the affine context, to define a distance between two points, we consider the difference between the position vectors of the points and we measure the norm of the resulting vector.
At this point we can think of the formula as follows:
Let A and B be two points in the affine plane.
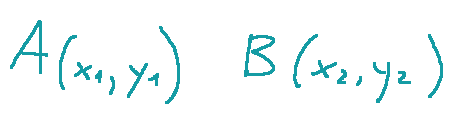
The distance d(A,B) is given by:
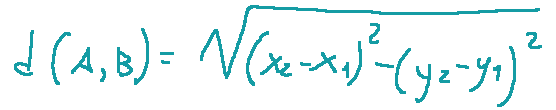
The implicit association to a Euclidean space combined with a defined metric gives this result. In the defined metric the concept of distance is consistent with the Pythagorean theorem.
Angles in the affine case
Now let's try to see how to measure the angle between two directions in the affine case. To do this, we use the scalar product between the vectors that represent those directions.
What is the scalar product?
Given an affine system associated with a Euclidean vector space, the scalar product between the following two vectors
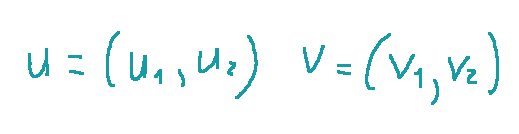
is defined as
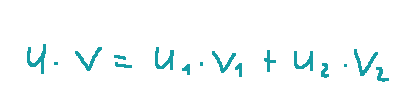
Cosine of the angle
Now let's see the formula for the cosine of the angle.
Let u and v be the vectors that represent two directions in the affine space.
The angle θ between them is given by:
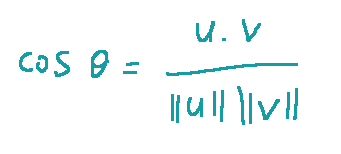
Where:
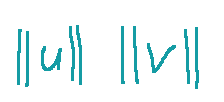
they are the norms of the vectors
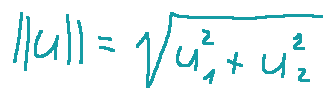
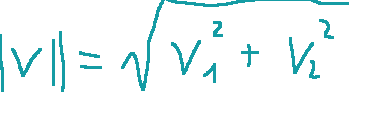
Conclusions
Regarding angles and distances in the affine case in analytic geometry, we can say the following:
Distances are measured using the Euclidean norm of the difference of position vectors.
Angles are calculated using the scalar product and the cosine relation.
Question
Have you studied linear algebra in the past and specifically angles and distances in the affine case?

[ITALIAN]
23-11-2024 - Education - Algebra lineare - Angoli e distanze nel caso affine [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei fornire alcune brevi nozioni a riguardo dell’argomento tecnico citato in oggetto.
Il contesto in cui operiamo è quello della geometria analitica o algebra lineare
(code notes: MOD-65)
Angoli e distanze nel caso affine
Nel contesto affine, per definire una distanza tra due punti, si considera la differenza tra i vettori posizione dei punti e si misura la norma del vettore risultante.
Distanze nel caso affine
Quando parliamo di geometria analitica e siamo nel contesto affine, per definire una distanza tra due punti, si considera la differenza tra i vettori posizione dei punti e si misura la norma del vettore risultante.
A questo punto possiamo pensare alla formula come segue:
Siano A e B due punti nel piano affine.
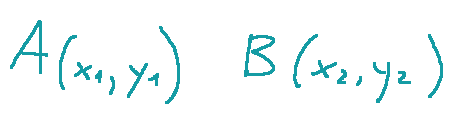
La distanza d(A,B) è data da:
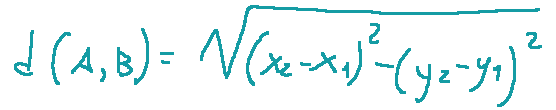
L’associazione implicita a uno spazio euclidea unita con una metrica definita fornisce questo risultato. Nella metrica definita il concetto di distanza è consistente con il teorema di Pitagora.
Angoli nel caso affine
Ora proviamo a vedere come fare per misurare l’angolo tra due direzioni nel caso affine. Per fare questo si utilizza il prodotto scalare tra i vettori che rappresentano quelle direzioni.
Cosa è il prodotto scalare?
Dato un sistema affine associato a uno spazio vettoriale euclideo, il prodotto scalare tra i due seguenti vettori
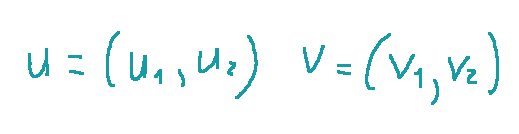
è definito come
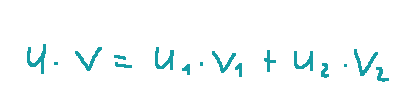
Coseno dell’angolo
Ora vediamo la formula per il coseno dell’angolo.
Siano u e v i vettori che rappresentano due direzioni nello spazio affine.
L’angolo θ tra di essi è dato da:
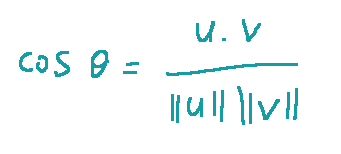
dove:
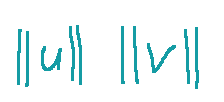
sono le norme dei vettori
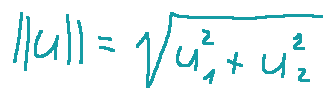
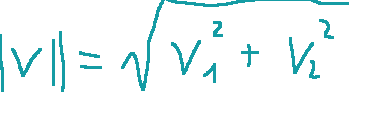
Conclusioni
Per quanto riguarda gli angoli e distanze nel caso affine in geometria analitica, possiamo dire quanto segue:
Le Distanze si misurano usando la norma euclidea della differenza dei vettori posizione.
Gli angoli si calcolano tramite il prodotto scalare e la relazione col coseno.
Domanda
In passato avete studiato l'algebra lineare e nello specifico gli angoli e distanze nel caso affine?
THE END
Comments