SLC S21 Week3 || Mastering Records and Record Arrays with Python
3 comments

Hello Steemians,
The Dynamic Dev team is pleased to present Week 3 of the Steemit Learning Challenge Season 21, focusing on mastering records and record arrays in Python. This challenge aims to deepen participants' understanding of structured data manipulation using Python's capabilities, without relying on Qt Designer.

I. Introduction to Records and Record Arrays
1. Definition and Importance
In programming, a record is a data structure that groups related data of various types under a single entity, similar to structures in languages like C. In Python, records can be represented using dictionaries, classes, or specialized structures like namedtuple and dataclass. When dealing with large datasets, especially in scientific computing, record arrays (structured arrays) in NumPy offer efficient storage and manipulation of heterogeneous data.
2. Why Use NumPy for Record Arrays?
The NumPy library is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python, offering powerful tools for creating and manipulating numerical data. Among its many features, NumPy provides structured and record arrays, which allow you to store complex, heterogeneous data within a single ndarray object. This capability is essential for efficiently handling structured datasets and performing vectorized operations on them.
II. Working with Records in Python
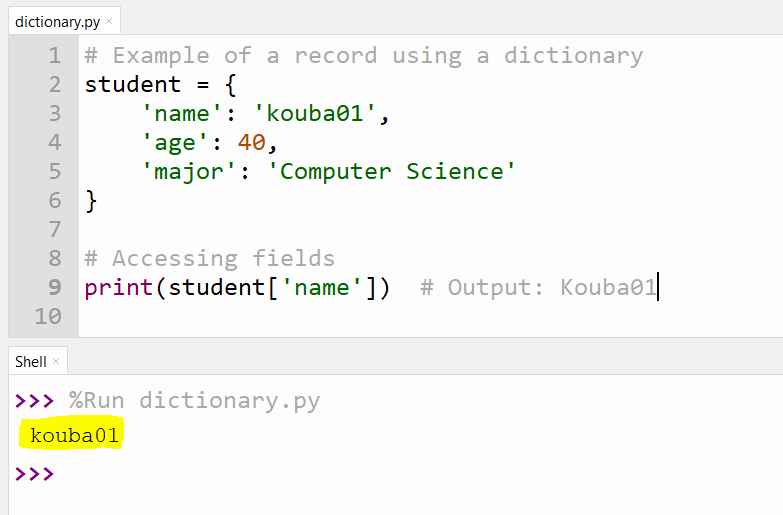
1. Using Dictionaries
Dictionaries in Python are versatile data structures that can be used to represent records. Each key-value pair corresponds to a field and its associated data.
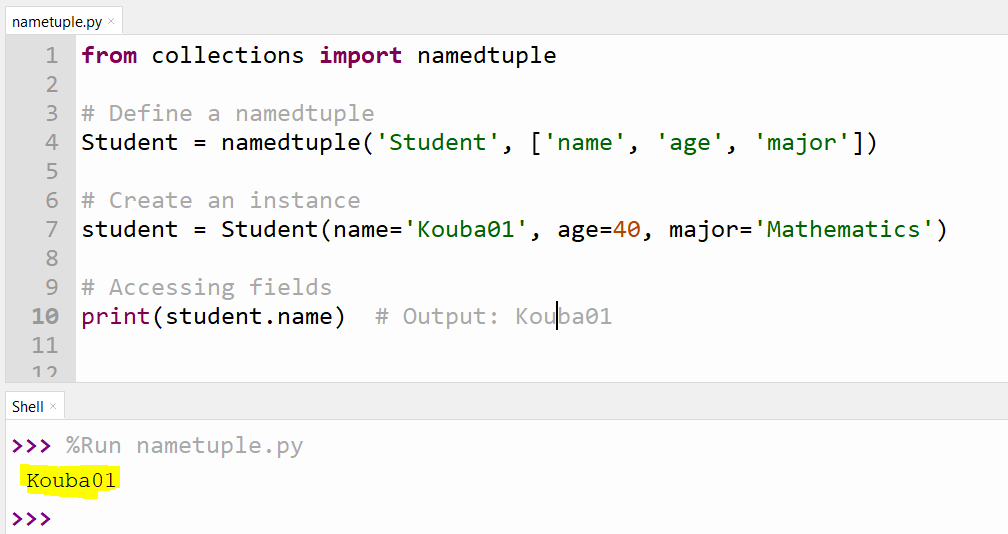
2. Using NamedTuples
The collections module provides namedtuple, which allows for creating tuple subclasses with named fields, offering both positional and named access to the data.
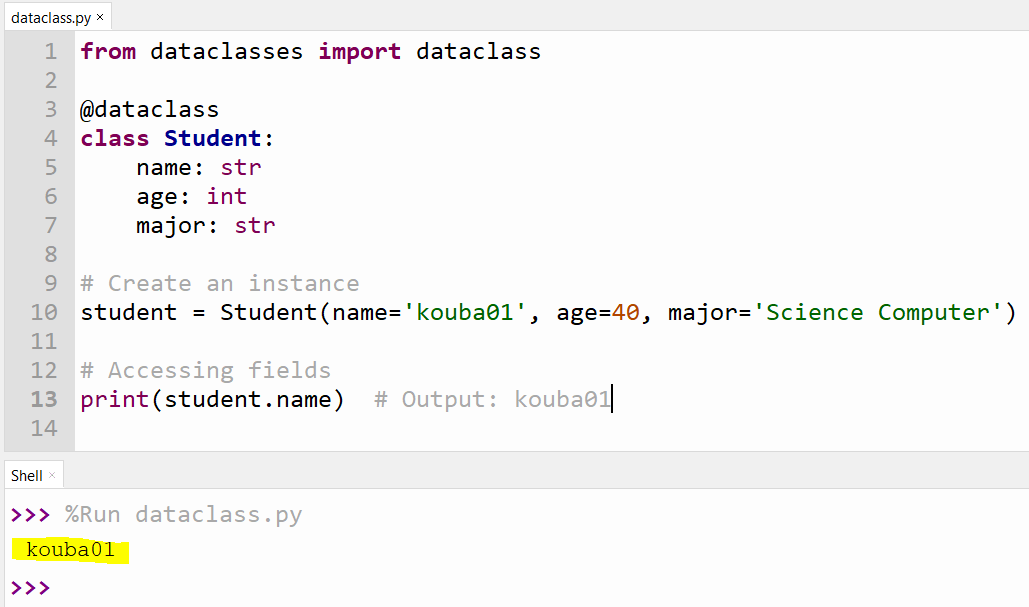
3. Using Data Classes
Introduced in Python 3.7, data classes provide a decorator and functions for automatically adding special methods to user-defined classes.
III. Working with Record Arrays in NumPy
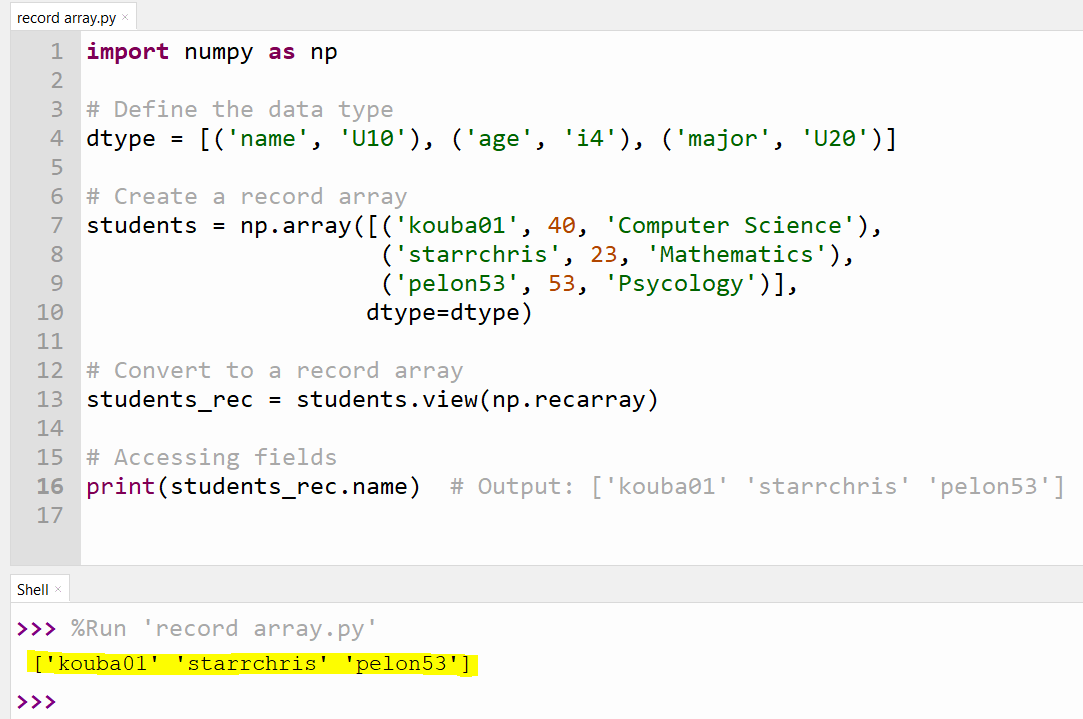
1. Creating Record Arrays
NumPy's recarray allows for the creation of arrays with fields accessible as attributes.
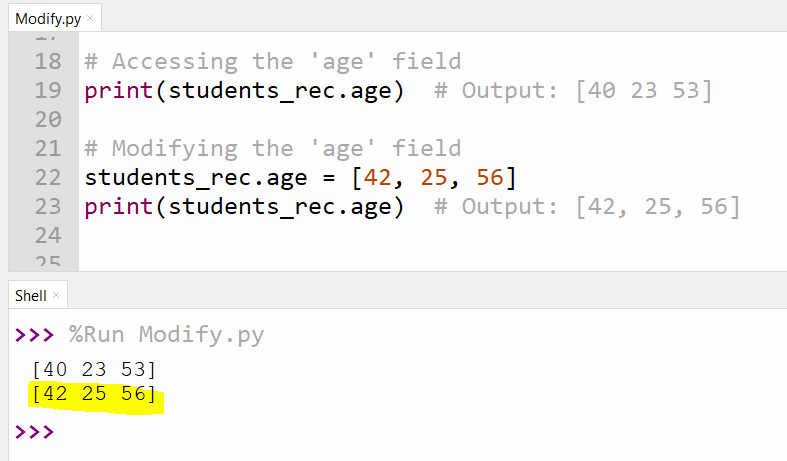
2. Accessing and Modifying Fields
Fields in a record array can be accessed and modified using attribute notation.
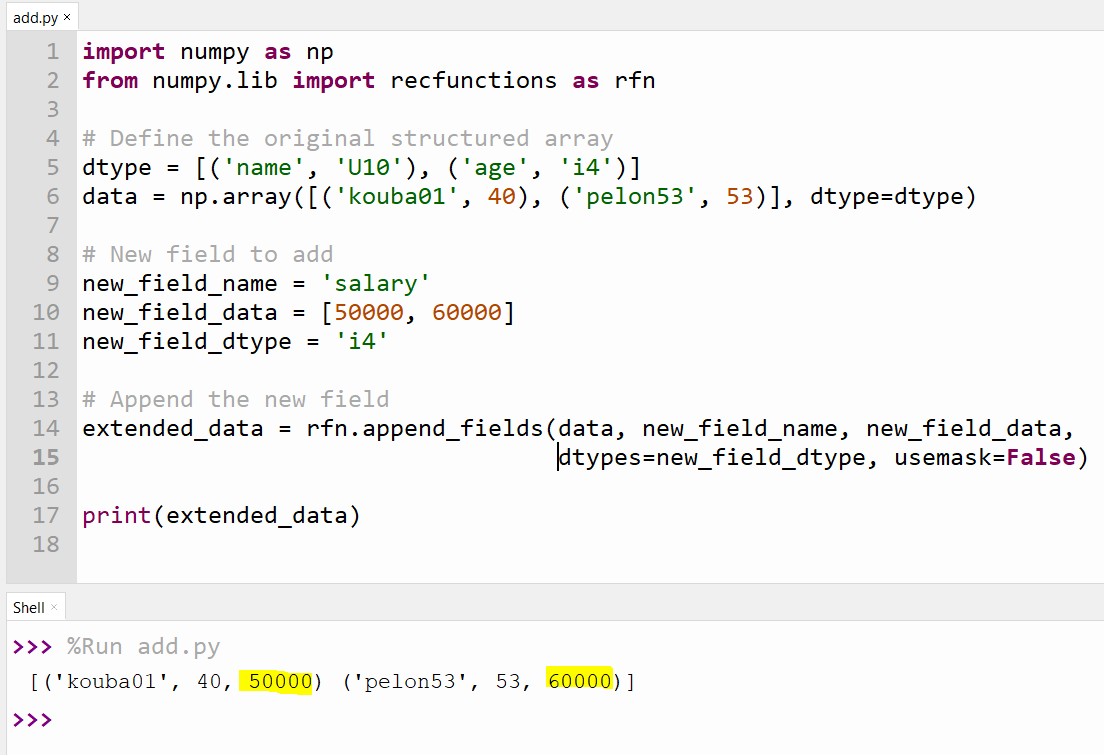
3. Adding New Fields
To add a new field to a record array, you can use the np.lib.recfunctions.append_fields function.

Homework :
Exercise 1: Advanced Employee Records Management (2points)
Objective: Develop a Python program to manage employee records using dataclass. The program should support adding, updating, and displaying employee information, along with calculating average performance scores and identifying top performers.
Requirements:
- Define a
dataclassforEmployeewith fields:id,name,position,salary, andperformance_scores(a list of floats). - Implement functions to:
- Add a new employee.
- Update an existing employee's information.
- Display all employees with their average performance scores.
- Calculate the average performance score for a specific employee.
- Identify and display top performers based on average performance scores.
- Use a list to store employee records.
Exercise 2: Comprehensive Student Grades Analysis (2points)
Objective: Utilize NumPy's structured arrays to store and analyze student grades, including calculating averages, identifying top students, and analyzing subject-wise performance.
Requirements:
- Create a structured array with fields:
student_id,name,math_grade,science_grade,english_grade, andhistory_grade. - Implement functions to:
- Calculate the average grade for each student.
- Identify students with average grades above a certain threshold.
- Determine the top student based on average grade.
- Analyze and display the average grade for each subject across all students.
- Identify subjects where students, on average, score below a passing grade.
Exercise 3: Enhanced Inventory Management System (2points)
Objective: Develop an inventory management system using namedtuple to track products, including functionalities for low stock alerts and identifying high-value products.
Requirements:
- Define a
namedtupleforProductwith fields:product_id,name,quantity,price, andcategory. - Implement functions to:
- Add new products.
- Update product quantities.
- Calculate the total inventory value.
- Generate low stock alerts for products below a certain quantity threshold.
- Identify the product with the highest total value (quantity × price).
- Provide a summary of inventory value by category.
- Use a list to store product records.
Exercise 4: Advanced Customer Orders Processing (2points)
Objective: Create a program to process customer orders using NumPy's structured arrays, including functionalities for calculating order totals, identifying large orders, and analyzing customer purchasing patterns.
Requirements:
- Define a structured array with fields:
order_id,customer_name,product,quantity,price_per_unit, andorder_date. - Implement functions to:
- Calculate the total price for each order.
- Identify orders exceeding a certain total amount.
- Determine the customer with the highest total spending.
- Analyze and display the total number of orders and total spending per customer.
- Identify products that are frequently ordered together.
Exercise 5: In-Depth Weather Data Analysis (2points)
Objective: Analyze weather data using dataclass and NumPy, including functionalities for calculating averages, identifying trends, and detecting anomalies.
Requirements:
Define a
dataclassforWeatherRecordwith fields:date,temperature,humidity,precipitation, andwind_speed.Create a list of
WeatherRecordinstances with sample data.Implement functions to:
- Calculate average temperature, maximum humidity, total precipitation, and average wind speed over a specified period.
- Identify days with temperatures above or below certain thresholds.
- Detect trends in temperature and precipitation over time (e.g., increasing, decreasing, stable).
- Identify anomalies such as sudden temperature spikes or drops.
Note: Each piece of source code written must be thoroughly explained line by line, emphasizing concepts that were previously covered in the course.

Contest Guidelines
Post can be written in any community or in your own blog.
Post must be #steemexclusive.
Use the following title: SLC S21 Week3 || Mastering Records and Record Arrays with Python
Participants must be verified and active users on the platform.
The images used must be the author's own or free of copyright. (Don't forget to include the source.)
Participants should not use any bot voting services, do not engage in vote buying.
The participation schedule is between Monday, November 11, 2024 at 00:00 UTC to Sunday, - November 17, 2024 at 23:59 UTC.
Community moderators would leave quality ratings of your articles and likely upvotes.
The publication can be in any language.
Plagiarism and use of AI is prohibited.
Use the tags #dynamicdevs-s21w3 , #country (example- #tunisia) #steemexclusive.
Use the #burnsteem25 tag only if you have set the 25% payee to @null.
Post the link to your entry in the comments section of this contest post. (very important).
Invite at least 3 friends to participate in this contest.
Strive to leave valuable feedback on other people's entries.
Share your post on Twitter and drop the link as a comment on your post.

Rewards
SC01/SC02 would be checking on the entire 17 participating Teaching Teams and Challengers and upvoting outstanding content. Upvote is not guaranteed for all articles. Kindly take note.
At the end of the week, we would nominate the top 4 users who had performed well in the contest and would be eligible for votes from SC01/SC02.
Important Notice: The selection of the four would be based solely on the quality of their post. Number of comments is no longer a factor to be considered.
Best Regards,
Dynamic Devs Team

Comments