SLC | S21W3 | Costs for entrepreneurs - Costing methods
2 comments
Assalam-o-Alaikum |
|---|
First of all I want to thank the steemit blog for introducing us to new teachers especially since the third week of season 21 has started which I am going to participate in. There is no doubt that there are indeed new learning opportunities for us here. Among other excellent teachers are @yolvijrm

canva designing
Q.1 - What are costing methods and what is their importance? |
|---|
Costing Methods and Their Significance
Costing methods are important tools employed by business organizations to ascertain the cost of an output. They assist the business in explaining its costs, offering correct prices for products or services and containing expense. Costing is central to management and the key to business planning and control. Here’s a look at common costing methods and why they are important:
Types of Costing Methods
1. Job Costing:
This method is adopted where products are manufactured following an order received. They are normally cobblers jobs or project based, and the costs are normally quoted per project. For instance, in construction business, cost may vary depending on each and every project by means of productive materials, and amount of workforce needed for the certain project.
2. Process Costing:
Applied where costs are spread over produce being produced for instance in production lines, manufacturing, or chemical production processes. The units are uniform with no differentiation of costs in the course of the manufacturing process. This method is suitable for the food processing industries and textile industries.
3. Activity-Based Costing (ABC):
ABC distributes overhead expenses to products with the activity necessary in product manufacturing. This method affords richer cost information in that it emphasises cost-driving activities, which makes it suitable for industries with high overhead and convoluted activity process.
4. Standard Costing:
Standard costing involves charging standard costs to products or services which are anticipated costs. This method is used in comparing the real costs with the standardized costs so as to evaluate efficiency and control for variances. The most commonly applied of the two is the Oscar based budgeting and it’s more often used for performance metrics.
5. Marginal Costing:
Then, in marginal costing there are only variable costs which are taken into account while fixed costs are not. When planning on whether to produce more of a good in a certain period, organizations use this method for costing or profitability.
Importance of Costing Methods
Costing methods are vital for multiple reasons:
Pricing Strategy: Right costing helps to price products right in order to cover cost of producing the products plus the desired degree of profit.
Profitability Analysis: Enables business organizations to determine their wining and losing products or services, to facilitate portfolio management.
Cost Control: Cost control accompanies understanding of costs and allows managing companies and improving their results through reduction of costs.
Budgeting and Forecasting: Costing methods also makes eventual budgeting and the consequent planning easier and effective.
Informed Decision-Making: They aid in decision making processes when it comes to production, pricing policies and harzardous activities.
Q.2 - Explain the difference between the job order and process costing methods. |
|---|
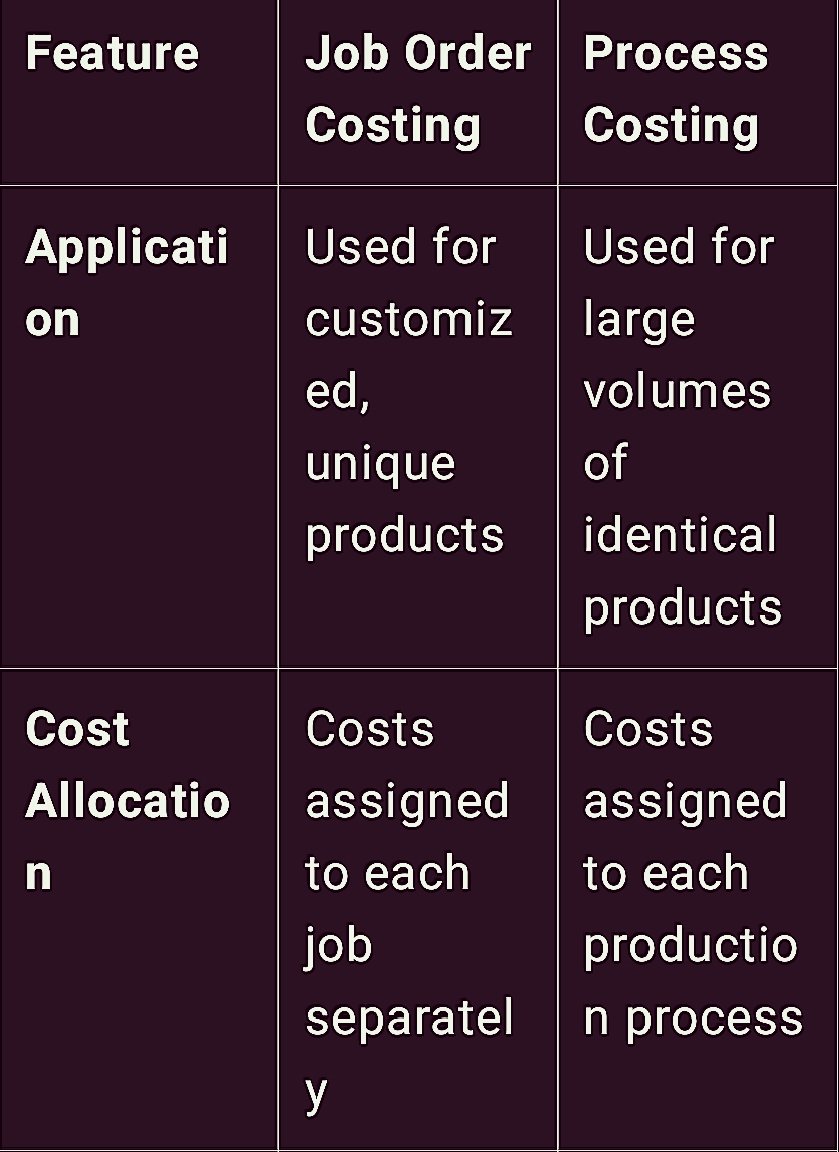
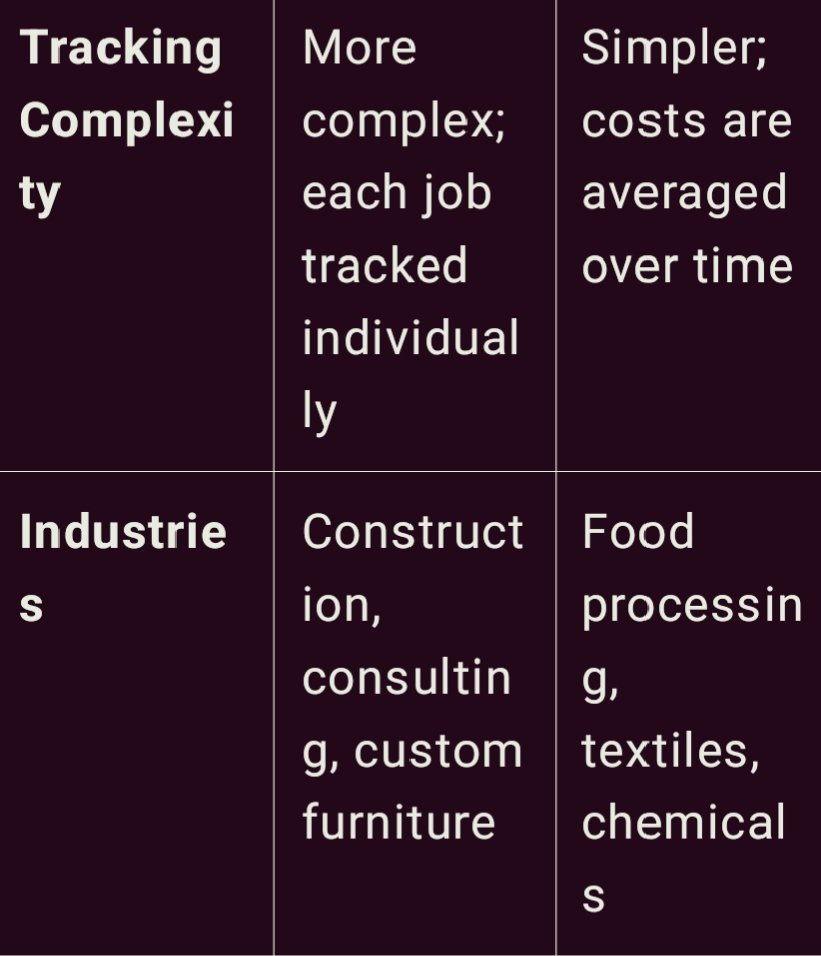
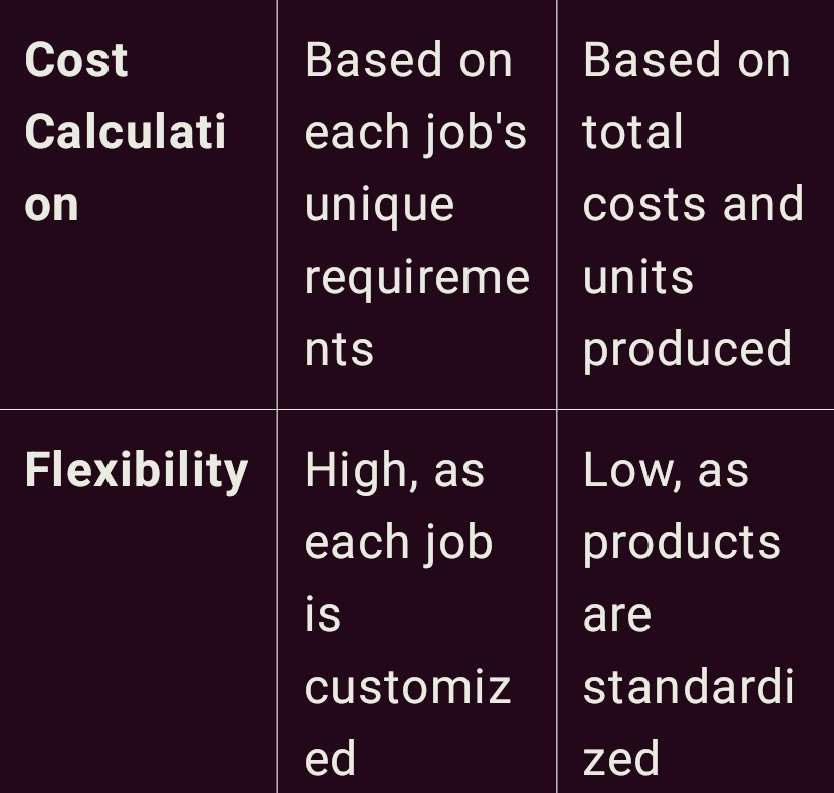
Job Order Costing vs. Process Costing:
Job order costing and process costing are two methods of cost accumulation that are used in the production process. Each of them has its own purpose and is used based on the type of production process occurring in a particular business. Here are detailed descriptions of both, as well as a comparison table.
Job Order Costing
Job order costing is applied in industries where units of production are special, and each is separate from the other. When every product or job is unique, then it will be most suitable for companies such as construction firms, custom furniture makers, or even most consultant businesses. The odd feature of this method is that each job is accounted separately, each job has its own costs, different from the other job’s costs.
Under job order costing, all costs incurred in the production process are attributable to each particular job namely; direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs. For example, a custom furniture shop would allocate costs of wood, labor hours and other overheads (equipment maintenance, etc) to a particular job, say, a table. It makes it easier to assign accurate cost for a particular product or service, in the overall pricing strategy.
Process Costing
Process costing on the other hand is more appropriate where products are standardized and produced in operation Zambia’s large scale industries such as the food processing industry, chemicals industry or textile. While the cost of job cost is affiliated to a particular job, process cost deputed costs to each process involved in production. Expenses are built up for a period and spread over all products manufactured within that period.
From the process costing discussion, we deduce that this approach assumes that all units produced are of equal value and costs are shared across all units. For instance in a juice factory, the cost of processing, bottling and packaging are determinants over all the bottles that are produced within a certain time frame.
Comparison Table
job order costing is advantageous for companies who take order based jobs since it gives a complete picture of the cost assigned to each job where as process costing is useful for companies that deal with continuous mass production since their cost can be apportioned amongst different units. It was established that choosing the right type of costing would provide better financial information and correct pricing.
Q.3 - Research and explain, to the best of your understanding, two costing methods different from those explained in this class. |
|---|
Certainly! Here’s an overview of two costing methods that might not typically be covered in standard classes: Target costing and Throughput costing.
Target Costing
Target costing is another type of pricing strategy that starts with the desired price and then builds from there a viable cost structure which is suitable for a particular good or service to be offered. In as much as target costing differs from traditional costing approach in which the costs incurred in production form the basis of the final price, target costing is very much customer driven. It is most widely used in highly competitive and fast-moving industries such as electronics and automobile industries.
This is followed by decision on the target selling price depending on market situation and other competitive influences. From this, the company subtracts its necessary profit margin to get the target cost; the maximum price the company can allow to produce the product and still make profits. This method calls for integration of various functional units such as design, engineering, manufacturing at an agreement of particular cost without necessitating compromise of quality. This is because cost targets can be set at the initial design stage of a project hence total cost control is facilitated. It also helps to foster cost leadership innovations that maintains customer value proposition squarely in view. However, one of the drawbacks of ABM is the difficulty of reaching target costs, especially in fluctuating industries of materials.
Throughput Costing
The throughput costing which is sometimes referred to as “super-variable costing” takes only the direct material costs as the product costs and deems all other costs such as the labor and overhead as the period costs. This is done in accordance with the Theory of Constraints (TOC) which posits that the rate at which a system processes customer orders through sales is the most critical overall the system. Throughput costing directs the companies to give attention to the bottleneck, and helps highlight where the concentration has to be made regarding high leverage factors in manufacturing rather than … [Focusing on the allocation of costs which are fixed and variable across all units manufactured].
This method has its utility because it fosters operation efficiency and allows managers to concentrate on other matters influencing profit. Further, it reduces costs and making estimates of costs, easier and faster, while identifying where cost is trapped in a company’s production processes. Throughput costing may not be preferable for organizations with high labour or overhead expense because it excludes these costs from product costing and can lead to misguiding profit indications in traditional accounting uses.
Every business function can benefit from target costing and throughput costing as cost management methods, as these tools provide optimal support to achieve operation and strategic objectives aimed at increasing profitability and improving throughput.
Q.4 - Perform the costing by work orders, according to what was explained for a cake manufacturing business |
|---|
Costing by Work Orders in Cake Manufacturing
Having known several costing techniques in cake manufacturing one theory is the costing by work orders where all costs in relation to specific orders are identified. This approach is said to be particularly useful in the context of cake businesses that entail production of individually tailored products whose prices can now be correctly pegged together with costs. This is how it can be arranged for a cake business displaying some important cost structures that come under the overall cost .
Key Cost Components
1. Materials Cost: This is all the ingredients that go go into the product batter such as flour, sugar, eggs, butter etc to exactly what the customer wants to top or decorate the cake with. The amount to be allocated to each cake should therefore be accurate by recording the quantity used for each cake sold.
2. Labor Cost: Wages depend on the amount of time bakers, decorators, and other employees working in the business take to complete a particular bakery product. For instance, the elaborated cake requires more material and time to prepare than a plain cake.
3. Overhead Cost: Cost of overhead can also be referred as indirect cost that encompass electricity, water bill, rent, and maintenance of equipment. These are generally given according to the proportion of the cost or time attached to each type of cake.
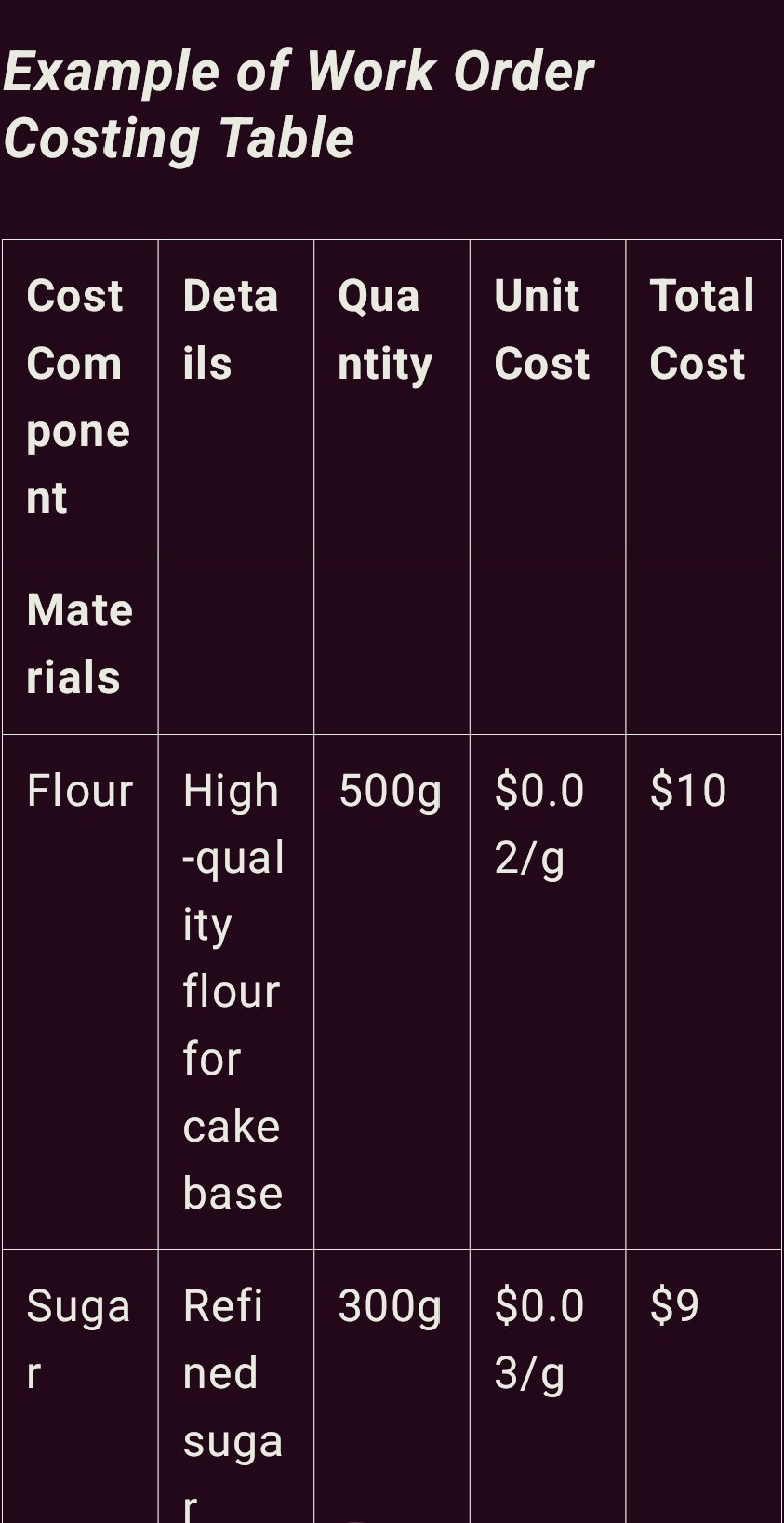
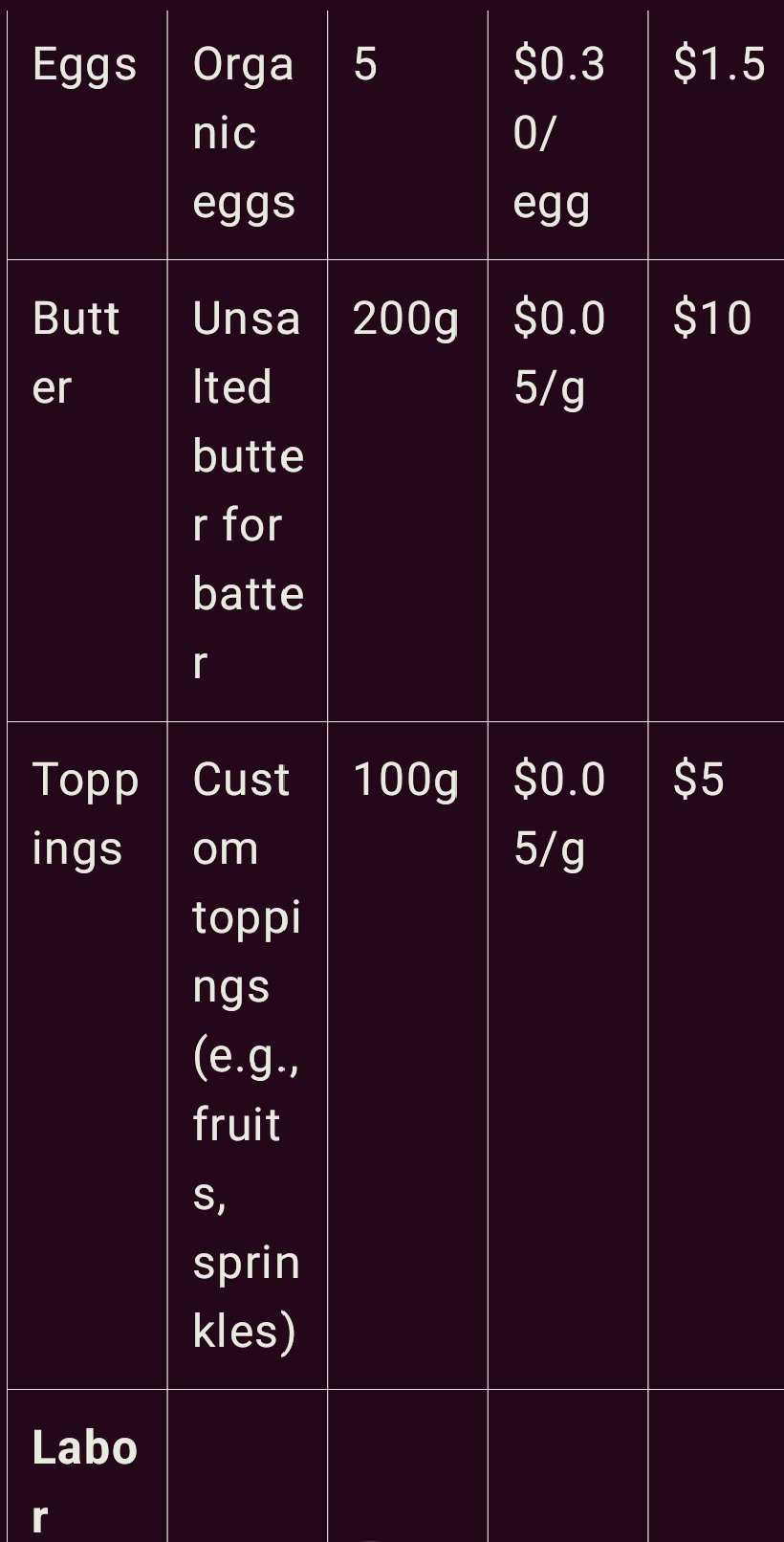
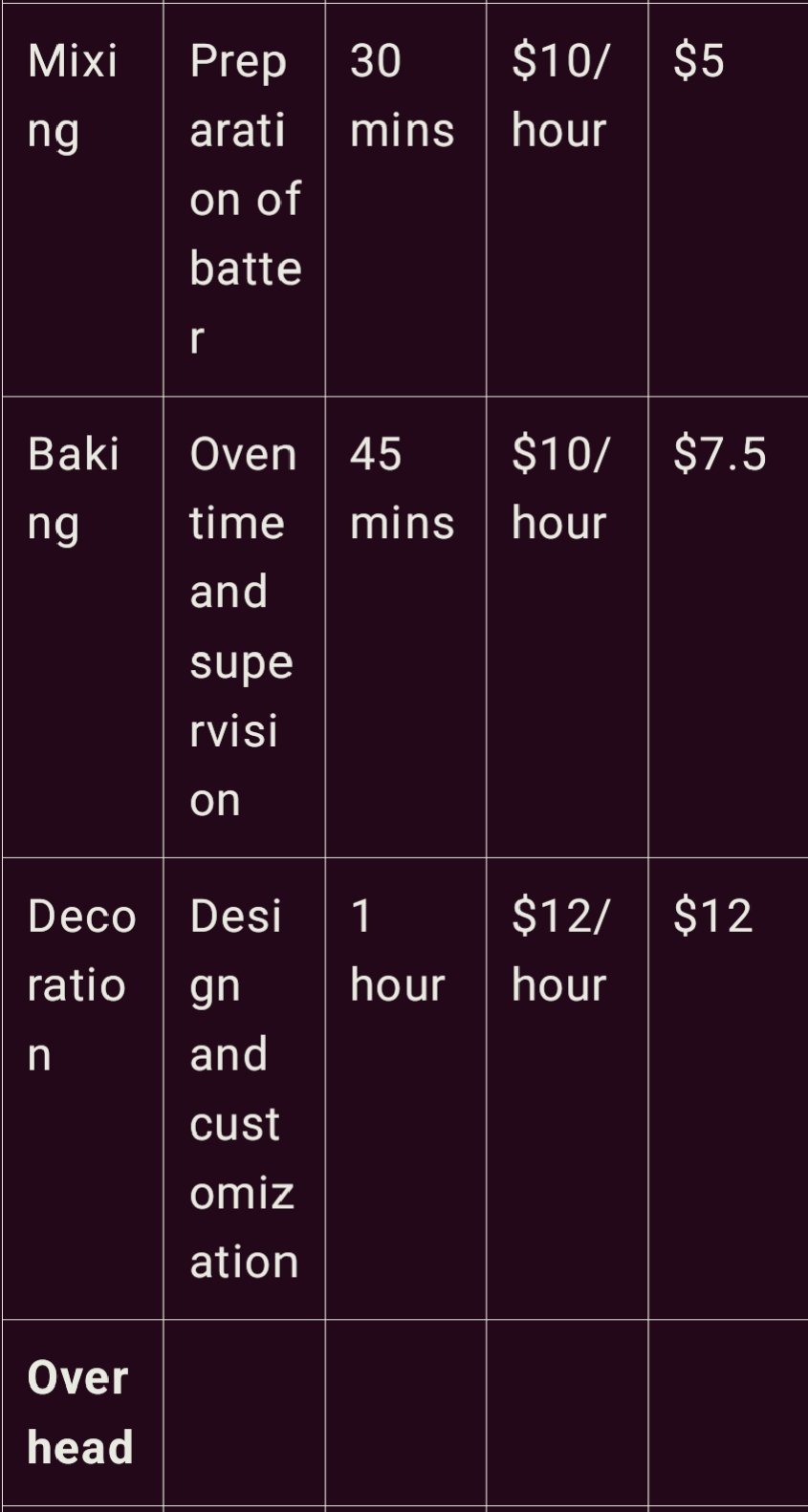
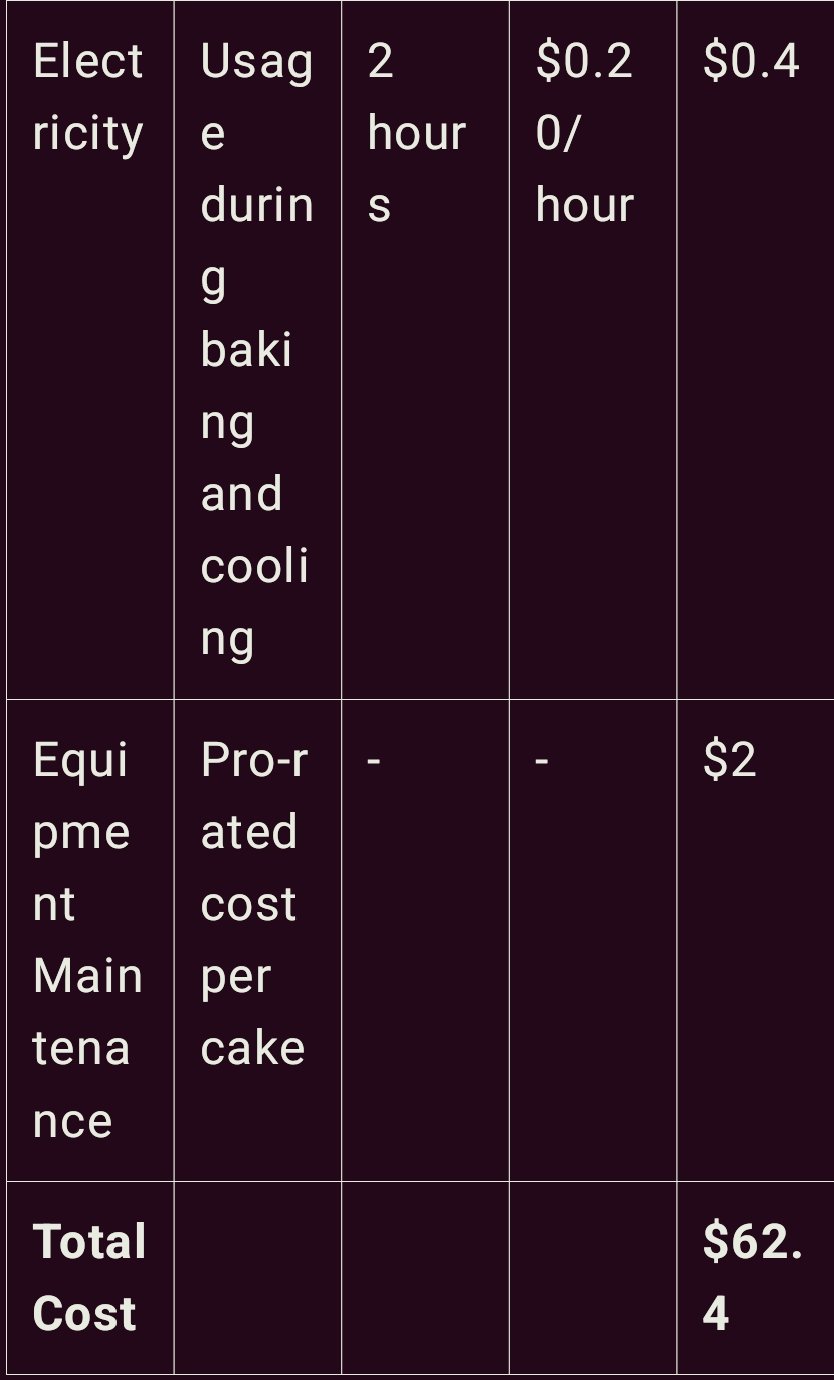
Some of the specific work order costing information that could be included in a firms computerized system are as follows;
Analysis
Here’s how this table works: This table indicate the capture of each cost and how they enhance the total cost of the final product. For instance, if a cake order contains specific or better kind of ingredients the material cost is going to be high. Likewise, labor has direct relation with the type of cake and overhead is shared proportionately with reference of usage of tools and electricity consumption.
Work order costing is essential to cake manufacturers because it allows them to know the exact costs related to each order to price the products competitively and get the right price from customers.
i would like to invite @patjewell @wilmer1988 @stef1 to take part in this contest
Regard for me @shabbir86 |
|---|
Comments