ARN molecule found in an asteroid for the first time
2 comments
(NASA Goddard, JAXA, Dan Gallagher https://bit.ly/3JFDKr0)
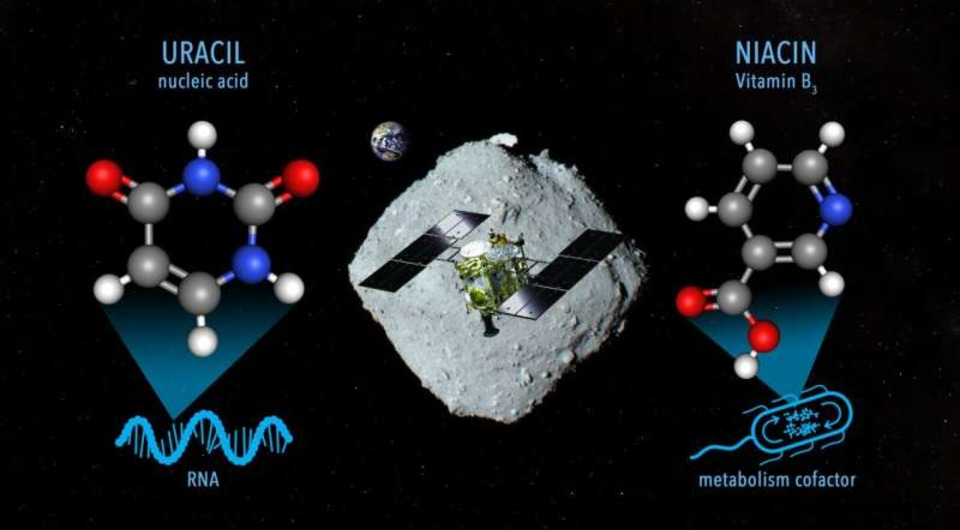
Japanese scientists have discovered uracil (one of the azocyst bases of RNA) in the substance of the asteroid Ryugu, as well as its isomers, nicotinic acid and its derivatives.
These substances expand the zoo of organic matter found on asteroids and formed in Ryugu through a series of abiotic processes.
The discovery made by researchers from the University of Hokkaido supports the idea that carbonaceous asteroids could have delivered organic matter to the young Earth.
The question of what role comets and asteroids played in the origin of life on Earth remains without a detailed answer.
To understand this problem, scientists analyze the substance of meteorites found on Earth.
However, more valuable data can be obtained by examining the primary substance of small bodies brought to Earth by automatic vehicles.
"Hayabusa-2" became the third such device and it delivered to Earth 5.4 grams of the substance of the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu.
Previously, amino acids were found in the Ryugu substance.
THE FINDINGS
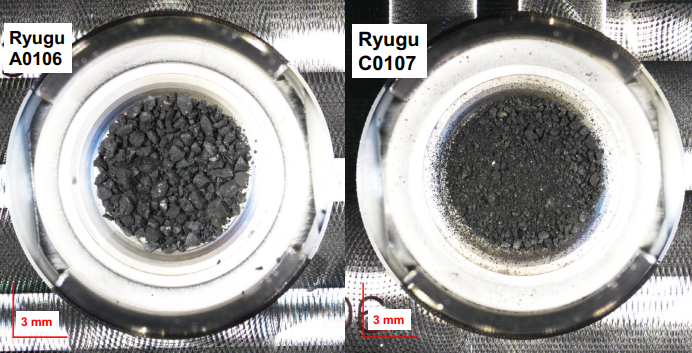
Now, a team of planetary scientists led by Yasuhiro Oba searched for nitrogen-containing organic compounds and their homologues in samples A0106 and C0107 taken from the surface of Ryugu and from its near-surface layer.
The scientists used high resolution mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry of isotopic composition with electrospray ionization in combination with liquid chromatography.
Both samples contained uracil, one of the four nitrogenous bases of ribonucleic acid.
The concentration of uracil was 7-11 and 21-32 ppb in A0106 and C0107, respectively, which is less than in the case of the Orgei meteorite.
(Yasuhiro Oba et al. / Nature Communications, 2023 https://bit.ly/3lvyQVD)
Structural isomers of uracil, imidazole-2-carboxylic acid and imidazole-4-carboxylic acid, were also found.
Other nitrogenous bases of DNA/RNA were not found.
The study also found nicotinic acid (concentration 49-99 ppb) and its structural isomer isonicotinic acid (concentration 49-62 ppb).
However, nicotinamide and its structural isomers were not found.
The difference in the content of uracil in different layers of Ryugu is associated with a difference in the intensity of exposure to regolith of external factors.
Those factors can be heating by solar radiation, or bombardment by ultraviolet photons and cosmic rays.
Organic matter in the near-surface Ryugu layer was more protected from these factors.
Sources:
- Nature Communications: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36904-3
- Phys: https://phys.org/news/2023-03-rna-molecule-uracil-asteroid-ryugu.html
- Astrobiology: https://astrobiology.com/2023/03/uracil-has-been-found-in-asteroid-ryugu-samples.html
Wanna relax, sleep or improve your focus?
Check this rain sound video: https://bit.ly/rainsfocus
Comments